Quiz Answer Key and Fun Facts
1. A is for Aardwolf. What is the aardwolf's diet?
2. B is for Bushbaby. Where, in South Africa, are bushbabies found?
3. C is for Civet. Which statement is true about the civet?
4. D is for Dassie. Which animal is the dassie most closely related to?
5. E is for Elephant. How do elephant matriarchal herds interact with each other, when meeting up?
6. F is for Fox. Which two species of fox are found in South Africa?
7. G is for Giraffe. Which statement best describes a giraffe's social or herd characteristics?
8. H is for Hippopotamus. What, when and how do hippos eat?
9. I is for Impala. Which statement best describes the horns of the impala?
10. J is for Jackal. Which Jackal species has a wider distribution in South Africa?
11. K is for Kudu. What does a kudu look like?
12. L is for Leopard. It is said that a leopard can't change its spots. What do these spots look like?
13. M is for Mongoose. The dwarf mongoose is the smallest, weighing in at only 220 - 350 grams. Which is the largest of the mongooses listed below?
14. N is for Nyala. The nyala has white vertical stripes, and spiral horns, similar to a much larger antelope. Which type does it resemble in appearance?
15. O is for Otter. The largest otter in South Africa is the Cape clawless otter. Besides fish and crabs, what does the otter eat?
16. P is for Porcupine. Which of the following statements about porcupines is NOT true?
17. Q is for Quagga, an extinct animal resembling a zebra. Recent DNA testing from museum specimens and hides has revealed what about them?
18. R is for Rhinoceros. South Africa has two species of rhino, the white and the black. How many horns do they have?
19. S is for Suricate. What is the more common name for these animals?
20. T is for Tsessebe. What is a tsessebe?
21. U is for Ungulate, which literally means a hoofed animal. One of the two odd-toed ungulates in South Africa is the zebra; which is the other?
22. V is for Vervet Monkey. This is the most common monkey found in Southern Africa. What are its common characteristics?
23. W is for Warthog. How many warts does a warthog have?
24. Y is for Yellow House Bat. Which family does the yellow house bat belong to?
25. Z is for Zebra. Which zebra species are found in South Africa?
Source: Author
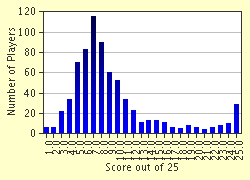
51percent
This quiz was reviewed by FunTrivia editor
crisw before going online.
Any errors found in FunTrivia content are routinely corrected through our feedback system.