The Air Up There Trivia Quiz
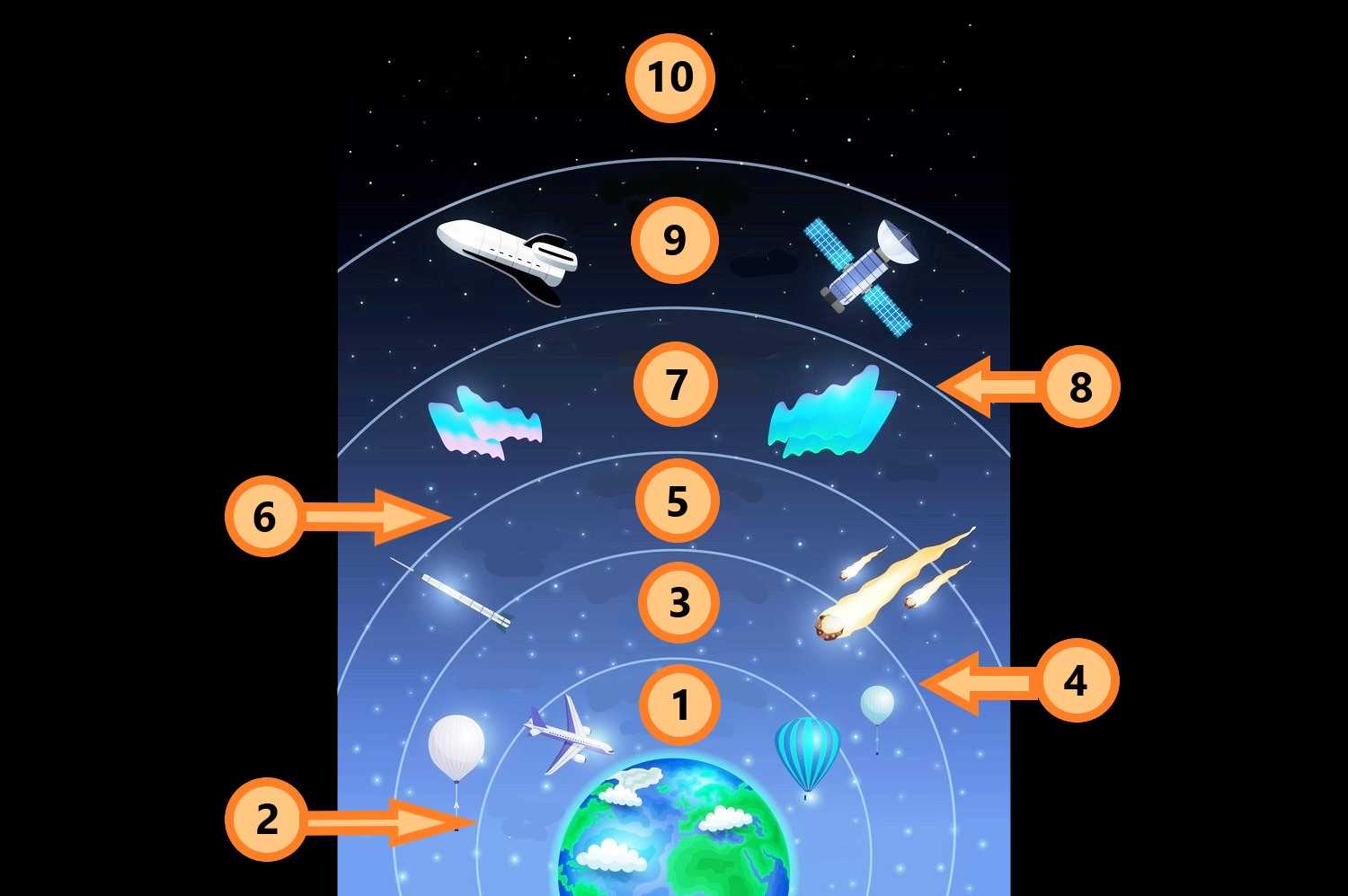
Earth's Atmospheric Layers
This educational quiz will help you learn about the layers of Earth's atmosphere! A helpful hint: The white lined barriers between the atmospheric layers contain the suffix "-pause".
A label quiz
by trident.
Estimated time: 3 mins.