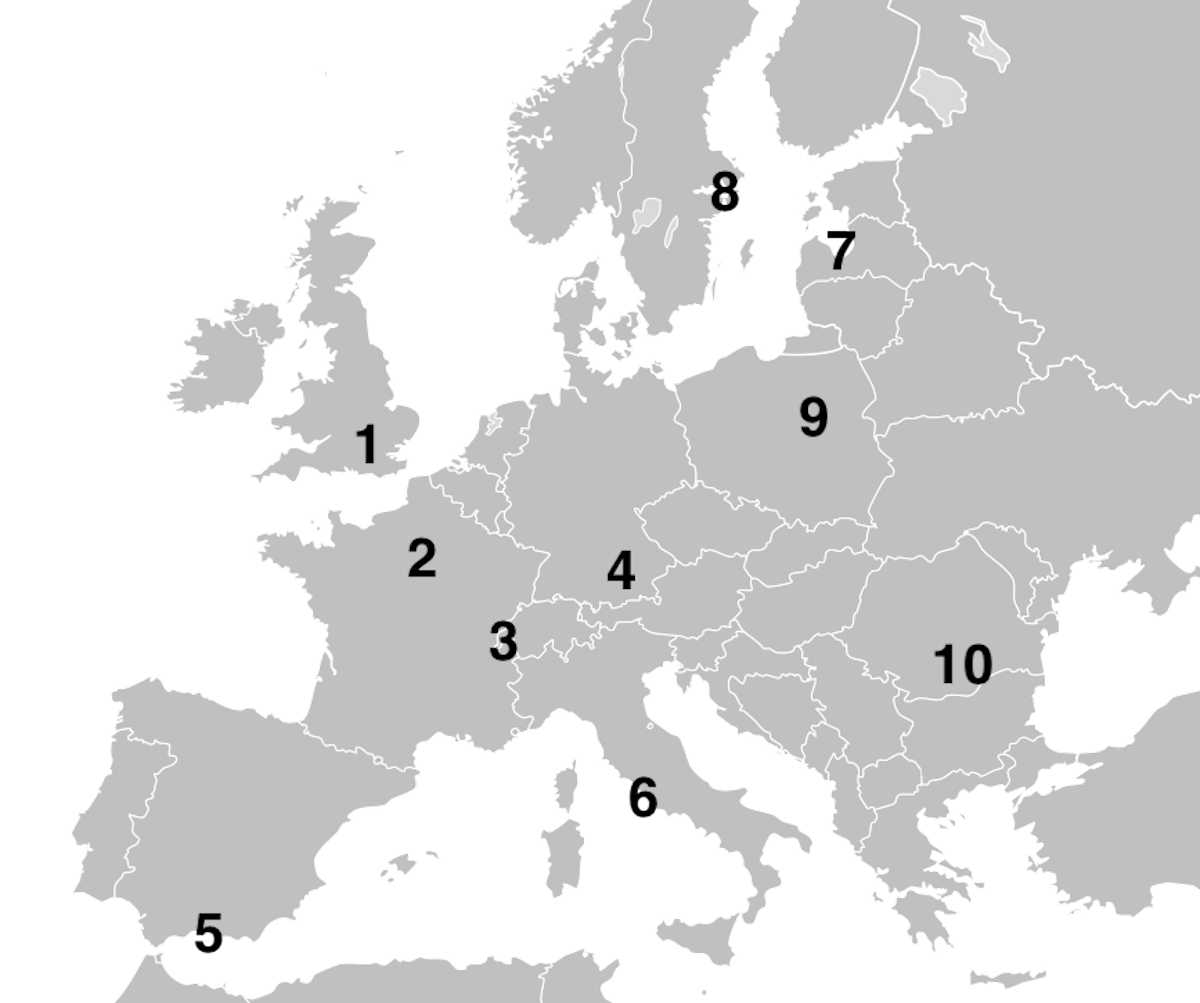
Where in Europe is FCO? Trivia Quiz
Can you match each IATA airport code to its correct location on the map of Europe?
This is a renovated/adopted version of an old quiz by author alanyo
A label quiz
by wellenbrecher.
Estimated time: 3 mins.