Quiz Answer Key and Fun Facts
1. In populations with a high incidence of malaria, there is a concurrent rise in the frequency of sickle cell trait as a sort of "natural defense mechanism." When human bones dating back at least 6,000 years were found in an eastern Mediterranean archaeological site, what was the indication they had come from a person with sickle cell trait?
2. About 3,600 years ago, Egyptians noticed that symptoms of malaria (high fever, shaking chills, nausea, etc.) increased in prevalence during which natural phenomenon?
3. Among many other great achievements, this academician was first to describe the manifestations of malaria and categorize the characteristic fever. Who was this influential physician?
4. Ah, Peru, land of mountains, ancient ruins, and the ever-enigmatic Nazca Lines. It is also the area from which native Peruvians developed the first effective cure for malaria in 1600 - the ground bark of the cinchona tree. What alkaloid, now known to combat the infection, is contained within?
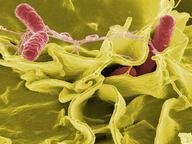
5. 1907 Nobel Laureate Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran, son of a renowned army doctor, researched malaria in Constantine, Algeria. In 1889, he was awarded the Bréant Prize for discovering the then-disputed cause of the infection. What microscopic invaders give rise to malaria?
6. One of the more unorthodox treatments for an infectious disease came at the hands of another Nobel Laureate, Julius Wagner-Jauregg. He inoculated people infected by Treponema pallidum with the agent responsible for malaria and let the fever rage until the heat-sensitive spirochete died. Wagner-Jauregg then eliminated the malaria. What disease did this unusual method cure?
7. With the advent of new antimalarial drugs in World War II, certain soldiers discovered some particularly nasty side effects. When administered mepacrine, for example, a man afflicted with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) deficiency would develop acute hemolytic anemia, rendering him incapable of doing anything useful. This genetic disorder is actually another safeguard against malaria, but unlike sickle cell trait, G-6-PD deficiency has dietary restrictions. Which of these foods is a must to avoid?
8. Which of these antimalarial drugs, first introduced in 1971, resembles quinine in structure and has the highest incidence of debilitating side effects?
9. Accidentally synthesized in 1874 by Othmar Zeidler, the chemical DDT was first found to have insecticidal properties more than half a century later. The Malaria Eradication Campaign of 1955 saw this mosquito-killer sprayed in numerous countries in which malaria was endemic, all but completely eradicating the disease by 1967. However, DDT had its opponents. What was the title of Rachel Carson's 1962 exposé of DDT's adverse effects on the environment?
10. Scientists have once again started to experiment with qinghao, a plant first used over 2,000 years ago in China as a cure for hemorrhoids. In the 341 AD medicinal handbook "Zhouhou Bei Ji Fang", it is recommended for use in "febrile illnesses." The active antimalarial agent was given the name "artemisinin" in the 1970s, after the plant's botanical name Artemisia annua (sweet wormwood). Does this spell good news for absinthe drinkers in malarious countries?
Source: Author
napkintosh
This quiz was reviewed by FunTrivia editor
crisw before going online.
Any errors found in FunTrivia content are routinely corrected through our feedback system.