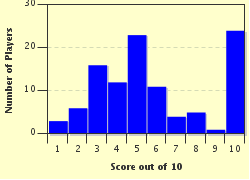
Quiz Answer Key and Fun Facts
1. Alanine is the second simplest amino acid (behind glycine), but there is a lot to it. Alanine scanning involves mutating certain amino acids in a protein to alanine. Why is this process very valuable to biochemists?
2. Phenylalanine is an aromatic amino acid, and is the precursor of several important substances in the body, such as dopamine and adrenaline. The first stage of synthesis for these substances often involves the conversion of phenylalanine into another amino acid by the addition of a hydroxyl group. Which amino acid is this?
3. Histidine is one of the more unique amino acids in terms of its chemical properties. It is also (by far) the most common amino acid at the active sites of those most remarkable proteins, the enzymes. Why is this?
4. Arginine is a basic amino acid and so usually exists in a positively charged form. It is also the most common amino acid at protein sites which bind to DNA (which is negatively charged). Which of the following proteins is least likely to bind DNA?
5. Glutamine has received much attention from medical groups in recent years owing to its relationship with a hereditary disease. Specifically, the number of consecutive glutamines in a certain protein determines whether or not a person has this disease, and (amazingly accurately) can be used to predict the age at which the person will begin to show symptoms. Such symptoms include mood swings (from aggression, to excitement, to apathy) and short-term memory loss. Which disease is this?
6. Tryptophan is the largest of the amino acids and is used to synthesise a range of molecules, such as NAD, which is important in cellular respiration. Tryptophan is also the precursor for what has become known as the "happiness molecule". Which molecule is this?
7. Proteases such as trypsin and chymotrypsin are important in bodily function as well as in analytical biology. Their biochemical mechanism is defined by an amino acid at their active site for which this group of proteases is named. Which amino acid is this?
8. Tyrosine is essential to the function of proteins such as the epidermal growth factor receptors and the insulin receptors. These proteins transmit signals from outside the cell and depend on substrate binding, receptor dimerization, and a modification of tyrosine. What is this modification?
9. One of the most commonly modified amino acids in proteins is lysine. Groups are added to lysine which can affect the function or the lifespan of a protein. Which of the following is NOT true about modification of lysines?
10. Methionine is important in methyl group transfer and in many aspects of metabolism. Methionine is also the "start" amino acid, meaning it is always the first amino acid incorporated into a protein. However, why is methionine not found at the start of every mature protein?
Source: Author
doublemm
This quiz was reviewed by FunTrivia editor
CellarDoor before going online.
Any errors found in FunTrivia content are routinely corrected through our feedback system.