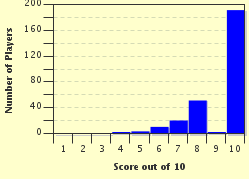
Among the Living Trivia Quiz
Among the living, you will find that body parts are organised into systems, groups that work together for some purpose. Match each organ to a human body system of which it is a part.
A matching quiz
by looney_tunes.
Estimated time: 3 mins.